年初为排查性能问题写了一个动态获取函数调用耗时的工具(Kirin)。工具主要包括两个部分:macOS应用,负责发送采集指令,格式化数据生成 Chrome Trace Viewer 用到的 Trace Event Format 格式的数据;framework动态库,嵌入到App里,负责接收指令,采集耗时数据。
使用的时候是直接将framework拖到项目里面运行项目就可以了,但是实际场景下Debug阶段可以通过Instrument更加的方便大多数时候需要定位生产版本的问题,就需要将现有的ipa包能动态将framework注入,然后将动态库拷贝到 Payload 的 Frameworks 目录下面,最后重签名后再安装到手机上进行测试。
关于动态注入framework这部分,使用的是 optool 这个工具,使用起来比较简单:
(1)下载源码
git clone https://github.com/alexzielenski/optool.git
cd optool
git submodule update --init --recursive
(2)编译可执行文件
cd optool
xcodebuild -project optool.xcodeproj -configuration Release ARCHS="x86_64 arm64" build
将 build/Release/optool 拷贝出来。
(3)执行下面的命令可以注入动态库
export PATH="${pwd}/bin:$PATH"
optool install -c load -p "@rpath/Kirin.framework/Kirin" -t Payload/Demo.app/Demo
如果需要移除对应的库可以使用:
optool uninstall -p "@rpath/Kirin.framework/Kirin" -t Payload/Demo.app/Demo
命令执行完成后,可以通过下面的命令查看framework注入/移除的情况:
otool -L Payload/Demo.app/Demo
大概的结果示例如下:
Payload/Demo.app/Demo
....
@rpath/Kirin.framework/Kirin (compatibility version 0.0.0, current version 0.0.0)
因为 optool 项目是开源的,而且核心实现就一个文件不到600行代码,其中 install 这部分的代码的核心实现在
BOOL insertLoadEntryIntoBinary(NSString *dylibPath, NSMutableData *binary, struct thin_header macho, uint32_t type);
对照命令的使用和实现简单分析一下背后的实现机制:
-p @rpath/Kirin.framework/Kirin 表示要加载的动态库路径
-t Payload/Demo.app/Demo 二进制文件的路径
-c load 表示的指定使用的 Load Command 类型为 LC_LOAD_DYLIB,可选的类型有:
-
(1) load (LC_LOAD_DYLIB): 表示加载 dylib
-
(2) weak (LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB):工作方式与LC_LOAD_DYLIB相同,但如果未找到 dylib,执行将继续而不会出现错误。
-
(3) reexport (LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB):代理(或重新导出)来自不同库的符号
-
(4) upward (LC_LOAD_UPWARD_DYLIB):在两个库相互依赖时使用(这称为 向上依赖)
由于仅支持四种 Load Command, 所以一开始就判断是否是上面四种 Load Command, 代码如下:
if (type != LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB &&
type != LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB &&
type != LC_LOAD_UPWARD_DYLIB &&
type != LC_LOAD_DYLIB) {
LOG("Invalid load command type");
return NO;
}
接下来判断我们要添加的 Load Command 是否存在,如果存在就直接返回
// parse load commands to see if our load command is already there
uint32_t lastOffset = 0;
if (binaryHasLoadCommandForDylib(binary, dylibPath, &lastOffset, macho)) {
// there already exists a load command for this payload so change the command type
uint32_t originalType = *(uint32_t *)(binary.bytes + lastOffset);
if (originalType != type) {
LOG("A load command already exists for %s. Changing command type from %s to desired %s", dylibPath.UTF8String, LC(originalType), LC(type));
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(lastOffset, sizeof(type)) withBytes:&type];
} else {
LOG("Load command already exists");
}
return YES;
}
如果不存在,表示是新添加的 Load Command,目前支持的四种 Load Command ,都可以用 dylib_command 结构体来定义。
unsigned int length = (unsigned int)sizeof(struct dylib_command) + (unsigned int)dylibPath.length;
unsigned int padding = (8 - (length % 8));
加载命令在 Mach-O 文件加载解析时,会被内核加载器或者动态链接器调用。这些指令都采用 Type-Size-Value 这种格式,即:32 位的 cmd 值(表示类型),32 位的 cmdsize 值(32 位二级制位 4 的倍数,64 位位 8 的倍数),以及命令本身(由 cmdsize 指定的长度)。
其中 dylib_command 的定义如下:
union lc_str {
uint32_t offset; /* offset to the string */
char *ptr; /* pointer to the string */
};
struct dylib {
union lc_str name; /* library's path name */
uint32_t timestamp; /* library's build time stamp */
uint32_t current_version; /* library's current version number */
uint32_t compatibility_version; /* library's compatibility vers number*/
};
struct dylib_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_ID_DYLIB, LC_LOAD_{,WEAK_}DYLIB, LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes pathname string */
struct dylib dylib; /* the library identification */
};
在 MachOView 中呈现的结构如下所示:
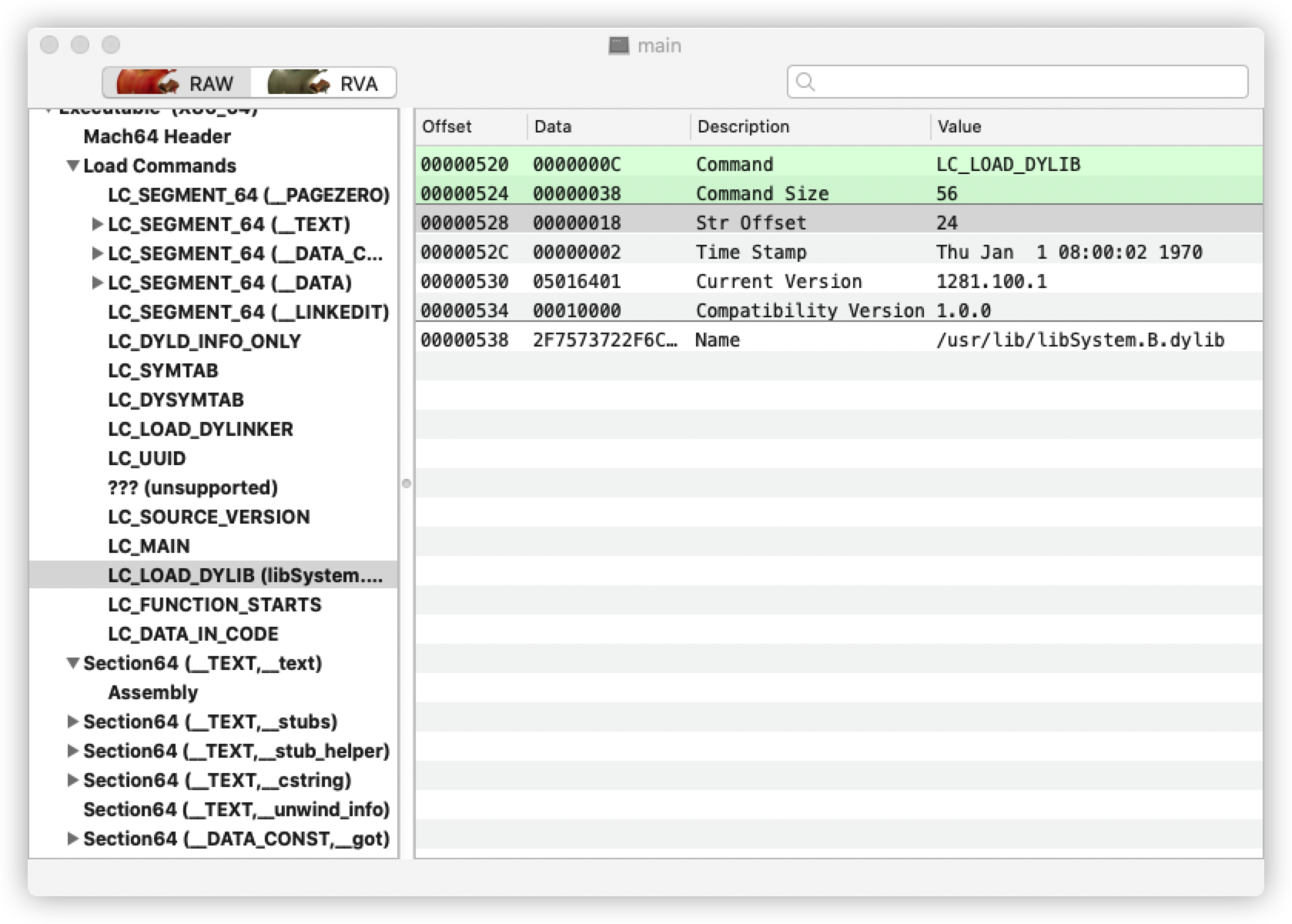
offset 指动态链接库字符串在 struct dylib_command 这个结构中的偏移
接下来就是判断 Load Command 段末尾是否还有空白位置
NSData *occupant = [binary subdataWithRange:NSMakeRange(macho.header.sizeofcmds + macho.offset + macho.size, length + padding)];
if (strcmp([occupant bytes], "\0")) {
NSLog(@"cannot inject payload into %s because there is no room", dylibPath.fileSystemRepresentation);
return NO;
}
无论是注入还是删除动态库链接,都不可以改变整个 Mach-O 文件的大小。这是因为在 Mach-O 文件中有很多内容是靠 offset 去定位的,如果改变了大小,那么那些 offset 就会失效,这样 Mach-O 文件就损坏了。所以,我们不可以添加或删除字节,只能覆写无用字节。因为 load_command 那块区域的尾部有一些全”\0”的字节区域(空白位置),所以,添加 dylib_command 就可以通过覆写这些”\0”字节完成。
创建 dylib_command ,并替换到对应位置的空白区域
struct dylib_command command;
struct dylib dylib;
dylib.name.offset = sizeof(struct dylib_command);
dylib.timestamp = 2; // load commands I've seen use 2 for some reason
dylib.current_version = 0;
dylib.compatibility_version = 0;
command.cmd = type;
command.dylib = dylib;
command.cmdsize = length + padding;
unsigned int zeroByte = 0;
NSMutableData *commandData = [NSMutableData data];
[commandData appendBytes:&command length:sizeof(struct dylib_command)];
[commandData appendData:[dylibPath dataUsingEncoding:NSASCIIStringEncoding]];
[commandData appendBytes:&zeroByte length:padding];
// remove enough null bytes to account of our inserted data
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(macho.offset + macho.header.sizeofcmds + macho.size, commandData.length) withBytes:0 length:0];
// insert the data
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(lastOffset, 0) withBytes:commandData.bytes length:commandData.length];
修正 header 内容,因为新增了一个 Load Command,所以 ncmds、sizeofcmds 要作对应的调整
// fix the existing header
macho.header.ncmds += 1;
macho.header.sizeofcmds += command.cmdsize;
// this is safe to do in 32bit because the 4 bytes after the header are still being put back
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(macho.offset, sizeof(macho.header)) withBytes:&macho.header];
以上就是 optool 注入一个动态库的大概流程。